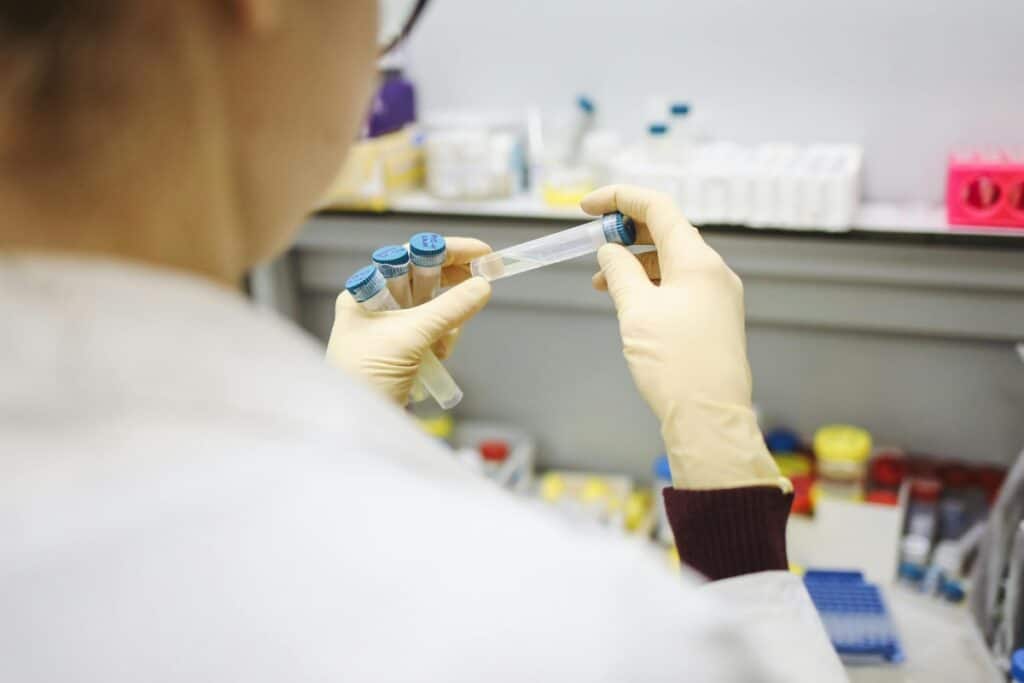
Ketamine, originally synthesized in 1962, was developed as an anesthetic by scientists searching for a safer alternative to phencyclidine (PCP). The synthesis of ketamine involves a complex chemical process that starts with cyclohexanone, a chemical compound derived from petroleum. Through a series of reactions, including condensation with o-chlorobenzonitrile, the creation of ketamine is achieved. The result is a unique compound with both anesthetic and analgesic properties, which has made it invaluable in both medical and veterinary fields.
In addition to its anesthetic uses, ketamine has been extensively researched for its potential in treating mental health conditions. Over time, it has evolved from being a battlefield anesthetic to a powerful tool in psychiatric treatment. Modern ketamine therapy, including the use of Spravato (esketamine), a nasal spray form, is derived from the same fundamental chemical process but is applied in innovative ways to address treatment-resistant depression and other mood disorders. The journey of ketamine from a synthesized chemical to a groundbreaking psychiatric treatment is a testament to its versatility and ongoing importance in medical science.
Discovery of Ketamine
The discovery of ketamine traces back to the early 1960s when Dr. Calvin Stevens, a chemist at Parke-Davis Laboratories, synthesized the compound while searching for safer anesthetic alternatives to phencyclidine (PCP). PCP was known for its effective anesthetic properties but also caused severe hallucinations and neurotoxicity. Dr. Stevens aimed to develop a compound that would retain the anesthetic benefits of PCP without its adverse side effects. His research led to the creation of ketamine, a molecule that would soon revolutionize anesthetic practices.
In 1965, Dr. Edward Domino conducted the first human trials of ketamine, observing its profound dissociative anesthetic effects. Unlike traditional anesthetics, ketamine induced a trance-like state where patients remained conscious but detached from pain and their surroundings. This discovery was groundbreaking, as it provided a new, safer anesthetic option with minimal respiratory depression, making it particularly useful in emergency and battlefield settings. Over the decades, ketamine’s unique properties have not only solidified its role in anesthesia but also paved the way for its use in treating a variety of psychiatric conditions, highlighting its multifaceted potential in medicine.
When Did Ketamine Become Popular in Medicine?
Ketamine became popular in medicine shortly after its discovery and initial human trials in the mid-1960s. By 1970, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) had approved ketamine for use as an anesthetic, and it quickly gained popularity in both human and veterinary medicine. Its unique properties made it particularly valuable in situations where traditional anesthetics posed higher risks, such as in emergency surgeries and on the battlefield during the Vietnam War. Ketamine’s ability to provide effective anesthesia without significantly depressing respiratory or cardiovascular function made it a preferred choice in these high-stress environments.
Beyond its initial applications, ketamine’s popularity surged again in the early 2000s as research began to uncover its potential in treating mental health disorders. Studies revealed that ketamine could produce rapid antidepressant effects, particularly in individuals with treatment-resistant depression. This led to a renewed interest in ketamine, culminating in the 2019 FDA approval of Spravato (esketamine) nasal spray for depression. The dual rise of ketamine in anesthetic and psychiatric medicine underscores its significant and evolving role in healthcare, making it a valuable tool for both acute and chronic conditions.
Is Ketamine Made in a Lab?
Yes, ketamine is made in a lab through a complex chemical synthesis process. The production of ketamine begins with the chemical compound cyclohexanone, which is derived from petroleum. This compound undergoes a series of chemical reactions, including a condensation reaction with o-chlorobenzonitrile, to form the intermediate products necessary for ketamine synthesis. These intermediates are then further processed through steps such as reduction and rearrangement to ultimately yield ketamine hydrochloride, the form commonly used in medical settings.
The lab-based synthesis of ketamine ensures that it is produced in a controlled, sterile environment, adhering to strict pharmaceutical standards. This control is crucial for ensuring the purity and safety of the ketamine used in both anesthetic and psychiatric treatments. The ability to produce ketamine in a lab allows for consistent quality and availability, making it a reliable and essential medication in various medical fields.
Can Ketamine Be Found in Nature?
No, ketamine cannot be found in nature. It is a synthetic compound created entirely through laboratory processes. Unlike some drugs that are derived from natural sources, such as plants or fungi, ketamine does not occur naturally and requires chemical synthesis for its production. The development of ketamine involved deliberate design and synthesis by chemists aiming to create a safer anesthetic alternative to existing options like phencyclidine (PCP).
Is Esketamine Also Made in a Lab?
Yes, esketamine is also made in a lab. Esketamine is a stereoisomer of ketamine, meaning it is one of the two mirror-image forms of the ketamine molecule. Specifically, esketamine is the S-enantiomer of ketamine, which has been found to have more potent antidepressant effects compared to the R-enantiomer. The production of esketamine involves a sophisticated process of chemical synthesis and separation to isolate this specific enantiomer from the racemic mixture of ketamine.
The synthesis of esketamine follows similar principles to that of ketamine but includes additional steps to ensure the selective production of the S-enantiomer. This involves the use of chiral synthesis techniques or the separation of enantiomers from a racemic mixture. By isolating esketamine, scientists can harness its unique properties more effectively for medical use, particularly in the treatment of depression. The lab-based creation of esketamine ensures high purity and consistent quality, which is essential for its therapeutic applications.
Schedule Esketamine Therapy with Luxury Psychiatry
At Luxury Psychiatry Clinic, we are committed to providing the most advanced and effective treatments for mental health conditions. Among our cutting-edge therapies, we offer esketamine therapy through the FDA-approved medication, Spravato. This innovative treatment has shown remarkable results in helping individuals with treatment-resistant depression find relief and regain their quality of life.
Our team of experienced professionals is dedicated to ensuring that each patient receives personalized care tailored to their unique needs. If you or a loved one is struggling with depression and traditional treatments have not been effective, esketamine therapy at Luxury Psychiatry Clinic might be the solution. Contact us today to schedule a consultation and take the first step towards a brighter, healthier future.